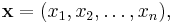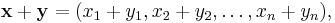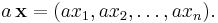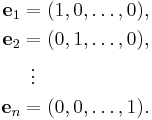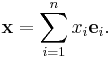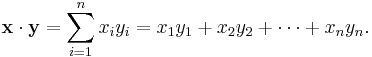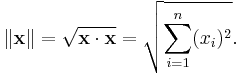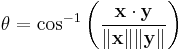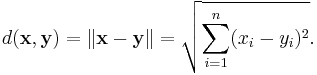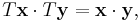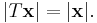Euclidean space
In mathematics, Euclidean space is the Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, as well as the generalizations of these notions to higher dimensions. The term “Euclidean” distinguishes these spaces from the curved spaces of non-Euclidean geometry and Einstein's general theory of relativity, and is named for the Greek mathematician Euclid of Alexandria.
Classical Greek geometry defined the Euclidean plane and Euclidean three-dimensional space using certain postulates, while the other properties of these spaces were deduced as theorems. In modern mathematics, it is more common to define Euclidean space using Cartesian coordinates and the ideas of analytic geometry. This approach brings the tools of algebra and calculus to bear on questions of geometry, and has the advantage that it generalizes easily to Euclidean spaces of more than three dimensions.
From the modern viewpoint, there is essentially only one Euclidean space of each dimension. In dimension one this is the real line; in dimension two it is the Cartesian plane; and in higher dimensions it is the real coordinate space with three or more real number coordinates. Thus a point in Euclidean space is a tuple of real numbers, and distances are defined using the Euclidean distance formula. Mathematicians often denote the n-dimensional Euclidean space by 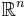 , or sometimes
, or sometimes 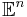 if they wish to emphasize its Euclidean nature. Euclidean spaces have finite dimension.
if they wish to emphasize its Euclidean nature. Euclidean spaces have finite dimension.
Contents |
Intuitive overview
One way to think of the Euclidean plane is as a set of points satisfying certain relationships, expressible in terms of distance and angle. For example, there are two fundamental operations on the plane. One is translation, which means a shifting of the plane so that every point is shifted in the same direction and by the same distance. The other is rotation about a fixed point in the plane, in which every point in the plane turns about that fixed point through the same angle. One of the basic tenets of Euclidean geometry is that two figures (that is, subsets) of the plane should be considered equivalent (congruent) if one can be transformed into the other by some sequence of translations, rotations and reflections. (See Euclidean group.)
In order to make all of this mathematically precise, one must clearly define the notions of distance, angle, translation, and rotation. The standard way to do this, as carried out in the remainder of this article, is to define the Euclidean plane as a two-dimensional real vector space equipped with an inner product. For then:
- the vectors in the vector space correspond to the points of the Euclidean plane,
- the addition operation in the vector space corresponds to translation, and
- the inner product implies notions of angle and distance, which can be used to define rotation.
Once the Euclidean plane has been described in this language, it is actually a simple matter to extend its concept to arbitrary dimensions. For the most part, the vocabulary, formulas, and calculations are not made any more difficult by the presence of more dimensions. (However, rotations are more subtle in high dimensions, and visualizing high-dimensional spaces remains difficult, even for experienced mathematicians.)
A final wrinkle is that Euclidean space is not technically a vector space but rather an affine space, on which a vector space acts. Intuitively, the distinction just says that there is no canonical choice of where the origin should go in the space, because it can be translated anywhere. In this article, this technicality is largely ignored.
Real coordinate space
Let R denote the field of real numbers. For any positive integer n, the set of all n-tuples of real numbers forms an n-dimensional vector space over R, which is denoted Rn and sometimes called real coordinate space. An element of Rn is written
where each xi is a real number. The vector space operations on Rn are defined by
The vector space Rn comes with a standard basis:
An arbitrary vector in Rn can then be written in the form
Rn is the prototypical example of a real n-dimensional vector space. In fact, every real n-dimensional vector space V is isomorphic to Rn. This isomorphism is not canonical, however. A choice of isomorphism is equivalent to a choice of basis for V (by looking at the image of the standard basis for Rn in V). The reason for working with arbitrary vector spaces instead of Rn is that it is often preferable to work in a coordinate-free manner (that is, without choosing a preferred basis).
Euclidean structure
Euclidean space is more than just a real coordinate space. In order to apply Euclidean geometry one needs to be able to talk about the distances between points and the angles between lines or vectors. The natural way to obtain these quantities is by introducing and using the standard inner product (also known as the dot product) on Rn. The inner product of any two real n-vectors x and y is defined by
The result is always a real number. Furthermore, the inner product of x with itself is always nonnegative. This product allows us to define the "length" of a vector x as
This length function satisfies the required properties of a norm and is called the Euclidean norm on Rn.
The (non-reflex) angle θ (0° ≤ θ ≤ 180°) between x and y is then given by
where cos−1 is the arccosine function.
Finally, one can use the norm to define a metric (or distance function) on Rn by
This distance function is called the Euclidean metric. It can be viewed as a form of the Pythagorean theorem.
Real coordinate space together with this Euclidean structure is called Euclidean space and often denoted En. (Many authors refer to Rn itself as Euclidean space, with the Euclidean structure being understood). The Euclidean structure makes En an inner product space (in fact a Hilbert space), a normed vector space, and a metric space.
Rotations of Euclidean space are then defined as orientation-preserving linear transformations T that preserve angles and lengths:
In the language of matrices, rotations are special orthogonal matrices.
Topology of Euclidean space
Since Euclidean space is a metric space it is also a topological space with the natural topology induced by the metric. The metric topology on En is called the Euclidean topology. A set is open in the Euclidean topology if and only if it contains an open ball around each of its points. The Euclidean topology turns out to be equivalent to the product topology on Rn considered as a product of n copies of the real line R (with its standard topology).
An important result on the topology of Rn, that is far from superficial, is Brouwer's invariance of domain. Any subset of Rn (with its subspace topology) that is homeomorphic to another open subset of Rn is itself open. An immediate consequence of this is that Rm is not homeomorphic to Rn if m ≠ n — an intuitively "obvious" result which is nonetheless difficult to prove.
Generalizations
In modern mathematics, Euclidean spaces form the prototypes for other, more complicated geometric objects. For example, a smooth manifold is a Hausdorff topological space that is locally diffeomorphic to Euclidean space. Diffeomorphism does not respect distance and angle, so these key concepts of Euclidean geometry are lost on a smooth manifold. However, if one additionally prescribes a smoothly varying inner product on the manifold's tangent spaces, then the result is what is called a Riemannian manifold. Put differently, a Riemannian manifold is a space constructed by deforming and patching together Euclidean spaces. Such a space enjoys notions of distance and angle, but they behave in a curved, non-Euclidean manner. The simplest Riemannian manifold, consisting of Rn with a constant inner product, is essentially identical to Euclidean n-space itself.
If one alters a Euclidean space so that its inner product becomes negative in one or more directions, then the result is a pseudo-Euclidean space. Smooth manifolds built from such spaces are called pseudo-Riemannian manifolds. Perhaps their most famous application is the theory of relativity, where empty spacetime with no matter is represented by the flat pseudo-Euclidean space called Minkowski space, spacetimes with matter in them form other pseudo-Riemannian manifolds, and gravity corresponds to the curvature of such a manifold.
Our universe, being subject to relativity, is not Euclidean. This becomes significant in theoretical considerations of astronomy and cosmology, and also in some practical problems such as global positioning and airplane navigation. Nonetheless, a Euclidean model of the universe can still be used to solve many other practical problems with sufficient precision.
See also
- Riemannian geometry
- Euclidean subspace
- Cartesian coordinate system
- Polar coordinate system
- Hilbert space